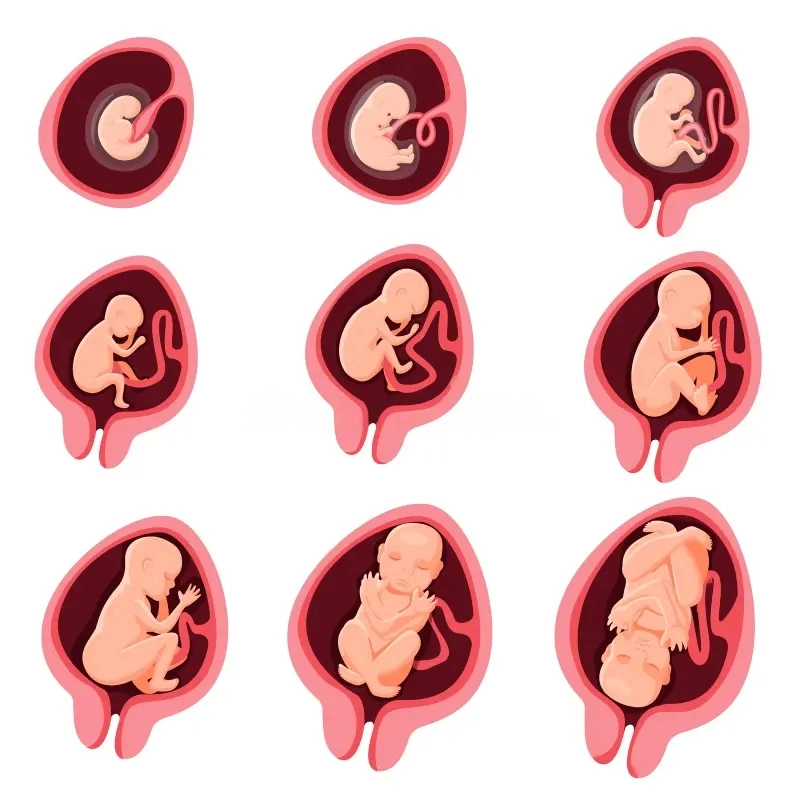
Stages of Embryonic Development
1. Fertilization
- The sperm and egg unite to form a zygote.
- Occurs in the fallopian tube.
2. Cleavage and Blastocyst Formation
- The zygote undergoes rapid mitotic divisions.
- Forms a blastocyst, which implants in the uterus.
3. Gastrulation
- Ectoderm (skin, nervous system)
- Mesoderm (muscles, bones, heart)
- Endoderm (digestive and respiratory systems)
4. Neurulation
- Development of the neural tube (future brain and spinal cord).
5. Organogenesis
- Formation of major organs and systems.
6. Fetal Development (Weeks 9-Birth)
- Rapid growth, refinement of organs, and development of functional systems.
Clinical Relevance
- Congenital Malformations (e.g., neural tube defects, heart defects)
- Assisted Reproductive Technology (e.g., IVF, stem cell research)
- Evolutionary Insights (Comparative embryology across species)
Embryology in Medicine and Research
Embryology helps in diagnosing genetic disorders, improving fertility treatments, and advancing regenerative medicine.
Embryology is the study of the formation, growth, and development of an embryo This branch of science deals with the primary prenatal stage, right from the formation of gametes (reproductive cells), fertilization, formation of the zygote (fertilized egg cell) to the development of embryo until blastocyst stage.


